Blog on RFID Technology and IoT Solutions
Blog Home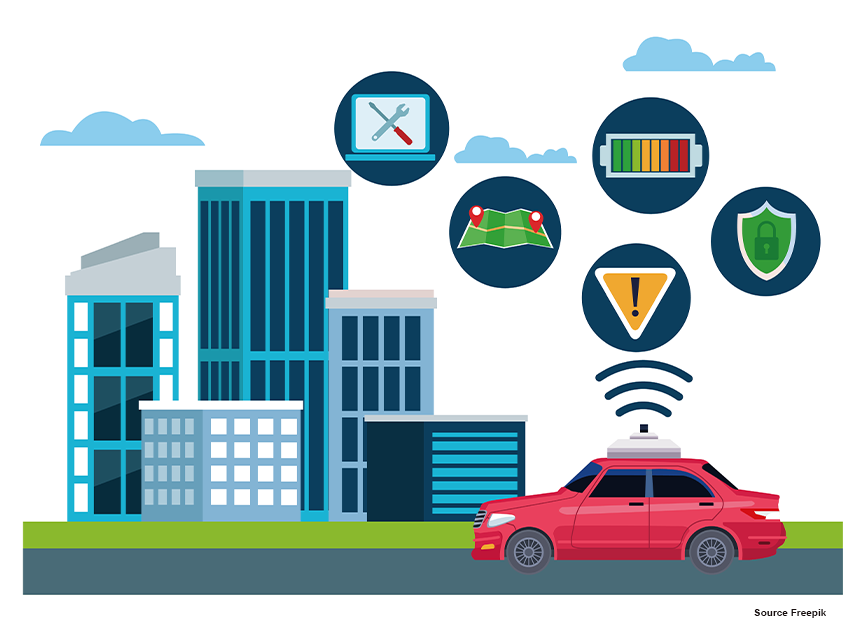
IoT in Automotive Industry
27 February 2023What is IoT in Automotive Industry?
IoT in Automotive Industry, or the Internet of Things, in the automotive industry refers to the integration of internet-connected devices and technology into vehicles. This can include things like wireless connectivity for infotainment systems, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and telematics for remote vehicle monitoring and control. The goal of IoT in the automotive industry is to improve the driving experience and make vehicles safer, more efficient, and more convenient for drivers and passengers.
Application of IoT in Automotive Industry and Future of Automobiles
IoT applications in the automotive industry are varied and include things like:
Connected Cars: Vehicles that can connect to the internet and share data with other devices and systems, such as traffic lights, other cars, and the cloud.
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS): IoT-enabled sensors and cameras can be used to enable features such as lane departure warning, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control.
Remote vehicle monitoring and control: IoT-enabled telematics can be used to remotely track and control a vehicle, allowing for things like remote diagnostics and the ability to remotely start or stop the engine.
Predictive maintenance: IoT sensors can be used to monitor a vehicle’s health, allowing for early detection of potential issues and proactive maintenance.
The future of automobiles is likely to be heavily influenced by IoT and other emerging technologies. Some of the key trends include:
Autonomous vehicles: IoT-enabled sensors, cameras, and communication technologies will be key to enabling fully autonomous vehicles.
Electric vehicles: IoT-enabled battery management systems and charging infrastructure will be essential for widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Smart cities: IoT-enabled vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication technologies will be critical for creating smart cities that can optimize traffic flow, reduce emissions, and improve safety.
Personalization: IoT-enabled vehicles will be able to gather data on driver behavior and preferences, allowing for a more personalized driving experience.
IoT Solutions for Automotive Industry
IoT solutions for the automotive industry can be broadly divided into two categories: those that focus on improving the driving experience, and those that focus on improving the vehicle’s performance and maintenance. Some examples of IoT solutions for the automotive industry include:
In-vehicle infotainment systems: These are systems that provide drivers and passengers with internet-connected entertainment and information services, such as navigation, music streaming, and social media.
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS): These are systems that use IoT-enabled sensors, cameras, and other technologies to improve vehicle safety, such as lane departure warning, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control.
Telematics and remote vehicle monitoring: IoT-enabled telematics systems can be used to remotely monitor and control a vehicle, allowing for things like remote diagnostics, vehicle tracking, and the ability to remotely start or stop the engine.
Predictive maintenance: IoT sensors can be used to monitor a vehicle’s health and detect potential issues, allowing for early detection of potential issues and proactive maintenance.
Electric Vehicle Charging: IoT-enabled EV charging stations and battery management systems can be used to optimize and monitor the charging of electric vehicles.
Smart Mobility: IoT-enabled V2I and V2V communication technologies will be critical for creating smart cities and optimize traffic flow, reduce emissions, and improve safety.
Cybersecurity: IoT-enabled vehicles will require robust cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and other cyber-attacks.
Automated logistics for fleet management: IoT-enabled systems for real-time tracking and management of fleet vehicles and cargo.
Conclusion
IoT solutions for the automotive industry have the potential to greatly improve the driving experience, increase vehicle safety and efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs. The implementation of IoT technologies in vehicles can range from connected infotainment systems to advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and predictive maintenance, to telematics and remote vehicle monitoring, to EV charging, Smart Mobility, and cybersecurity. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, IoT solutions will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of transportation. However, it’s important to consider the risks and challenges of these technologies such as cyber security threats, data privacy and ethical concerns, etc. To fully realize the benefits of IoT in the automotive industry, it will be necessary for manufacturers, suppliers, and regulators to work together to address these challenges and ensure the safe and secure deployment of these technologies.
- Intellistride.com
- Blog
- IoT in Automotive Industry